AI Basics: The Essential Beginner’s Guide

Table of Contents
Introduction
Let’s be honest—AI can feel like a huge, complicated, and even intimidating topic. It’s the kind of thing that makes people think of sci-fi movies, robot overlords, or ultra-complex algorithms running behind the scenes. But here’s the truth: AI is already part of your daily life, and whether you realize it or not, you interact with it dozens of times a day.
Think about it. When was the last time you Googled something? That’s AI at work. Used facial recognition to unlock your phone? AI again. Watched a Netflix show recommended just for you? Yup, AI.
But beyond these everyday conveniences, AI is also revolutionizing industries, changing the way we work, and even shaping the future of human intelligence itself. And that brings us to a critical point:
Understanding AI Basics isn’t just for techies or programmers anymore—it’s for everyone.
In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of AI, how it’s shaping the world today, and what the future holds. No technical jargon, no intimidating explanations—just a straightforward, engaging look at AI and why it matters to you.
1. What Is Artificial Intelligence? A Simple Explanation
If you’ve ever asked Siri for directions, watched a movie recommended by Netflix, or been amazed at how Google finishes your search query before you even type the full phrase, then you’ve already interacted with Artificial Intelligence (AI). But what exactly is AI, and how does it work?
At its core, AI is the science of creating machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence—such as recognizing speech, solving problems, making decisions, and even generating creative content. But AI isn’t about making robots that “think” exactly like humans. Instead, it’s about developing systems that can process massive amounts of information, learn from patterns, and improve over time without needing explicit instructions for every possible scenario.
Why Does AI Matter So Much?
To understand why AI has become such a hot topic, consider this: 90% of all the world’s data was generated in just the last two years. Humans simply can’t process and analyze that much information efficiently, but AI can. It helps businesses make smarter decisions, assists doctors in diagnosing diseases, predicts market trends, and even enhances our everyday experiences.
And here’s the real game-changer: AI is getting better at things we once believed only humans could do. When AI started, it was great at simple, repetitive tasks. But now, thanks to advancements in deep learning, AI can generate human-like text, create original music, and even paint pictures that look like they were crafted by professional artists.
But AI is not one single entity—it’s an umbrella term that covers many different technologies and approaches. Let’s break them down into digestible pieces.
2. A Brief History of AI: From Concept to Reality
AI didn’t just appear overnight—it has gone through decades of breakthroughs, failures, and moments of sheer brilliance. To appreciate how far we’ve come, let’s take a journey through AI’s remarkable history.
The Birth of the Idea (Pre-1950s): The Origins of AI
Believe it or not, the idea of AI goes back thousands of years. Ancient myths and legends often spoke of mechanical beings with human-like intelligence. The Greeks, for instance, told stories of Talos, a giant bronze automaton that protected Crete. In the Middle Ages, inventors tried to build mechanical “thinking” machines, and by the 19th century, mathematicians like Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace were laying the groundwork for computational thinking.
But the real birth of AI as a field of study happened in the 20th century.
The 1950s: The Era of Possibilities
The man widely regarded as the “father of AI” is Alan Turing. In 1950, he published his famous paper, Computing Machinery and Intelligence, where he proposed a fundamental question: “Can machines think?”
To answer this, he developed the Turing Test, a simple but brilliant idea—if a machine’s responses are indistinguishable from a human’s, does that mean it’s truly intelligent? This question still sparks debates today.
Meanwhile, in 1956, the term “Artificial Intelligence” was officially coined during the Dartmouth Conference, where pioneers like John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky outlined AI’s future. There was enormous excitement, and researchers believed that within a few decades, we’d have machines that could think just like humans.
The AI Winters: From Hype to Disappointment (1970s-1980s)
But reality hit hard. AI researchers overpromised and underdelivered. Early AI systems struggled with real-world unpredictability, and funding dried up. This led to the AI Winter, where progress stalled for almost two decades.
The 1990s-2000s: AI Gets Its Groove Back
The AI field came roaring back in the 1990s, thanks to two things: more computing power and better algorithms. In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue made history by defeating world chess champion Garry Kasparov—proving that machines could outthink humans in specific tasks.
2010s-Present: The AI Explosion
Now, we’re in the golden age of AI, where advancements in big data, deep learning, and cloud computing have enabled AI to surpass human performance in many areas—translation, medical imaging, and even creative writing. AI is no longer just science fiction; it’s an everyday reality.
3. How AI Works: The Core Technologies Behind It

So, how does AI actually work? The simplest answer: data + algorithms + computing power = AI magic. But let’s go deeper.
3.1 Machine Learning (ML) – The Brain of AI
Machine Learning (ML) is the heart of AI. Instead of programming a computer with explicit instructions, ML allows it to learn from data and improve over time.
Imagine teaching a child to recognize animals. Instead of listing every possible animal, you show them thousands of pictures, and over time, they start recognizing patterns. That’s exactly how ML works—it learns from experience.
The Three Main Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning: The AI learns from labeled data—for example, feeding an AI thousands of cat and dog pictures so it can recognize them in new images.
- Unsupervised Learning: The AI finds patterns in unlabeled data—for example, grouping similar customers based on shopping habits.
- Reinforcement Learning: The AI learns by trial and error—like how AlphaGo learned to play and dominate the game of Go.
3.2 Deep Learning – The Power of Neural Networks
Deep Learning is a subset of ML that uses Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) to mimic how the human brain processes information.
For instance, ChatGPT and DALL·E (which generates images) are powered by deep learning models trained on vast datasets, allowing them to understand language and create new content.
3.3 Natural Language Processing (NLP) – AI That Understands Us
NLP enables AI to process and respond to human language—and it’s getting scarily good.
For example:
- Google Translate: AI can now translate languages with near-human accuracy.
- Chatbots : They can hold conversations and even mimic specific writing styles.
The stat that blows my mind? By 2026, 90% of all online content could be generated by AI!
3.4 Computer Vision – AI That Sees the World
AI doesn’t just read and write—it can also see! Computer vision allows AI to analyze images and videos.
Some incredible applications:
- Medical AI detects cancer with over 95% accuracy—sometimes better than human doctors.
- Self-driving cars use AI to recognize traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
4. Common AI Applications in Everyday Life

Let’s be real—AI is everywhere, even if you don’t always notice it. From the moment you wake up to the time you go to sleep, AI is quietly working in the background, making your life more convenient, efficient, and even entertaining.
4.1 AI in Your Daily Routine
Smart Assistants: The AI That Talks to You
When you wake up and ask Alexa, Siri, or Google Assistant about the weather, you’re interacting with Natural Language Processing (NLP)—one of AI’s most impressive capabilities. These virtual assistants don’t just answer basic questions; they learn from your behavior, adapt to your habits, and improve their responses over time.
- Fun fact: Over 50% of all searches are now voice-based, and by 2024, voice assistants are expected to reach 8.4 billion devices—more than the human population!
AI in Social Media: The Invisible Content Curator
Ever wondered why TikTok, Instagram, or YouTube always seem to know what videos will keep you hooked? That’s AI at work! These platforms use machine learning algorithms to analyze your viewing habits, predict your interests, and serve you content that keeps you engaged for longer periods.
- A shocking stat: 35% of Amazon purchases and 80% of Netflix watch time come from AI-driven recommendations!
AI in Smart Homes: The AI That Learns Your Preferences
From smart thermostats like Nest that optimize your home’s temperature based on your routine, to AI-powered security cameras that recognize faces, AI is transforming the way we live.
One of the most exciting areas is AI-powered smart kitchens, where fridges can detect expired food, suggest recipes based on what you have, and even place grocery orders automatically.
4.2 AI in Work and Productivity
AI in Email and Communication
If you’ve ever noticed Gmail suggesting how to complete your sentences, you’ve used AI-powered text prediction. And tools like Grammarly use AI to improve your writing by analyzing tone, clarity, and grammar in real-time.
- Fun fact: AI-powered chatbots handle 85% of customer service inquiries, reducing wait times and improving efficiency.
AI in Finance: Smarter Money Management
From fraud detection to personalized investment recommendations, AI has revolutionized banking and finance. Apps like Mint and YNAB analyze your spending habits and offer budgeting tips, while AI-driven trading bots predict market trends faster than human analysts ever could.
- AI is estimated to save the banking industry $1 trillion by 2030.
4.3 AI in Healthcare: Saving Lives with Data
This is where AI truly shines.
- AI can analyze medical images (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans) with 95% accuracy, often outperforming human doctors.
- AI-powered chatbots like Ada Health help diagnose symptoms before you even see a doctor.
- AI assists in drug discovery, reducing development time from years to months.
A real-world impact? AI helped detect breast cancer in early stages 30% more effectively than traditional screenings.
5. The Ethical Concerns and Risks of AI
AI is amazing, but let’s not pretend it’s all sunshine and rainbows. With great power comes great responsibility, and AI brings serious ethical concerns.
5.1 The Bias Problem: AI Isn’t Always Neutral
Many people think AI is unbiased, but that’s a dangerous myth. AI learns from human-created data, which means it can inherit human biases.
Example: A hiring algorithm used by Amazon was trained on past hiring data—mostly male candidates—so the AI started favoring men over women.
- Studies show AI facial recognition is 98% accurate for white men but only 65% accurate for Black women—a massive issue in law enforcement and hiring.
5.2 Privacy Risks: AI Knows Too Much About You
AI is hungry for data. Every time you browse, search, or shop online, AI is collecting and analyzing your information. While this makes services more personalized, it also raises privacy concerns.
Think about it:
- Ever searched for a product and then saw ads for it everywhere?
- Your smart home devices are always listening—which can be exploited by hackers.
5.3 The Fear of Job Loss: Will AI Replace Humans?
Let’s be honest—some jobs are at risk. AI is already automating tasks that were once done by humans.
- By 2030, AI is expected to displace 375 million jobs worldwide.
- But here’s the twist: AI also creates new jobs—data scientists, AI trainers, machine learning engineers, and even AI ethicists.
The key? Adapt and learn AI-related skills.
6. How to Get Started with AI as a Beginner
AI sounds complex, but you don’t need a PhD to understand or use it. Here’s a beginner-friendly roadmap to getting started.
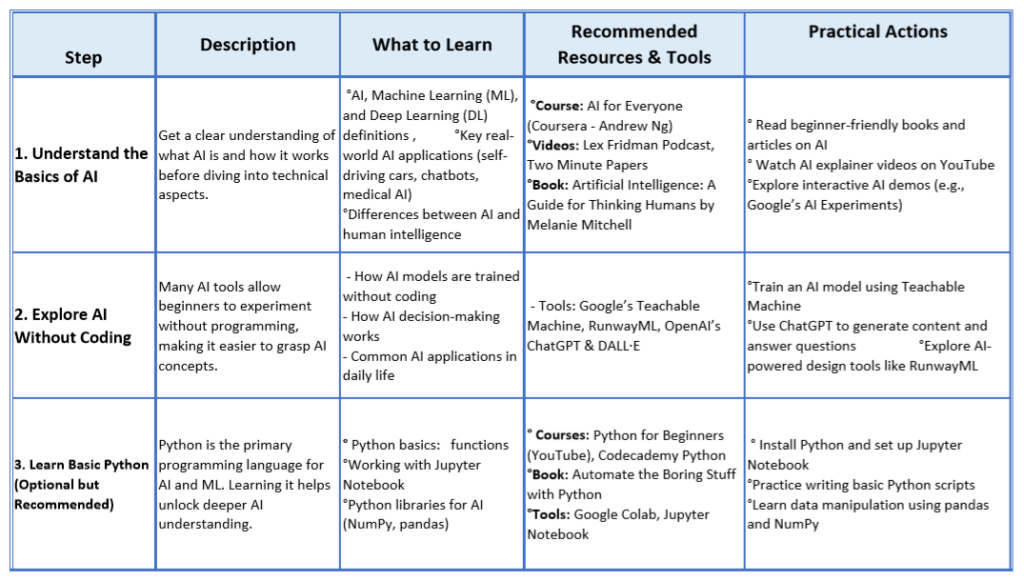
6.1 Understanding the Basics
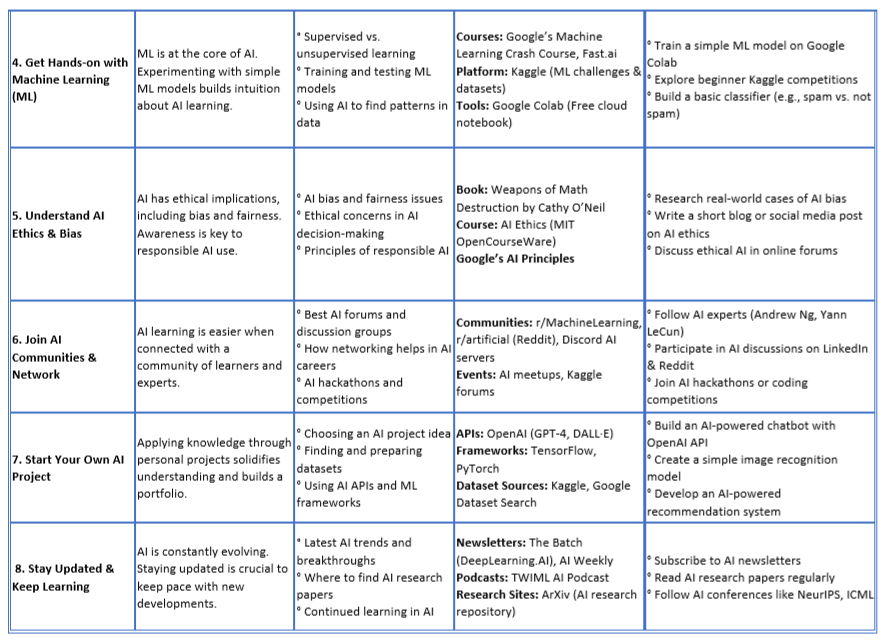
6.2 Hands-on AI Practice: Learn by Doing

7. The Future of AI: What’s Next?
Now, let’s talk about what’s coming next. AI has already transformed our world, but the truth is, we’re just getting started. The next decade will bring even more breakthroughs, ethical dilemmas, and paradigm shifts in how AI integrates with society.
So what does the future of AI actually look like? Let’s explore some of the most exciting (and sometimes terrifying) possibilities.
7.1 AI and the Workforce: A Double-Edged Sword
One of the biggest fears people have about AI is job automation. And let’s be real—it’s a valid concern.
- By 2030, AI is expected to replace up to 375 million jobs worldwide (McKinsey & Company).
- In some industries, like manufacturing and retail, automation is already displacing human workers.
But here’s the flip side: AI will also create new jobs—jobs we haven’t even imagined yet. Think about it this way:
- 100 years ago, jobs like “social media manager” or “data scientist” didn’t exist.
- With AI, new roles will emerge—AI ethicists, AI trainers, prompt engineers, and more.
The key? Adaptation. The best way to secure your future isn’t to fear AI—it’s to learn how to work with it.
7.2 AI and Creativity: The Rise of AI-Generated Content
- AI-generated art is winning competitions (a recent AI painting even won a fine art competition!).
- AI can now write music, compose poetry, and even script entire movies.
- Platforms like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Midjourney can create human-like content in seconds.
You might think of AI as something that handles math, logic, or automation, but it’s also diving into creative fields.
But here’s a hot take: AI won’t replace human creativity—it will enhance it.
- Think about photography: When cameras were invented, people feared it would replace painters. But instead, art evolved.
- AI in creativity will work as a tool, helping artists, writers, and musicians push their boundaries rather than replace them.
7.3 AI and Healthcare: A Revolution in Medicine
AI isn’t just about chatbots and smart assistants—it’s literally saving lives.
- AI can detect diseases faster than human doctors.
- Machine learning algorithms analyze medical scans with 95% accuracy.
- AI is revolutionizing drug discovery, reducing research timelines from years to months.
One incredible example? DeepMind’s AlphaFold—it solved the protein folding problem, a medical mystery that scientists had struggled with for 50 years!
The future of AI in healthcare is mind-blowing. We’re talking about personalized medicine, AI-assisted surgeries, and even AI-powered mental health support.
Imagine a world where:
- AI can predict diseases before symptoms appear.
- Virtual AI doctors provide instant, accurate diagnoses.
- AI-powered prosthetics and brain-computer interfaces enhance human abilities.
This isn’t sci-fi anymore—it’s happening right now.
7.4 AI and Ethics: The Biggest Challenge Ahead
For all its incredible potential, AI also comes with serious risks.
The Bias Problem
AI is only as good as the data it’s trained on. And if that data is biased, AI will be too.
- Facial recognition AI is 98% accurate for white men but only 65% accurate for Black women—a huge issue in policing and hiring.
- AI-driven hiring tools have been shown to favor men over women, reinforcing workplace discrimination.
If we don’t address these biases, AI could unintentionally reinforce inequality instead of solving it.
The Privacy Issue
AI collects and analyzes massive amounts of personal data—but who controls it?
- AI listens to your conversations, tracks your searches, and even predicts your emotions.
- In China, AI-driven surveillance is being used for mass citizen monitoring—a dystopian warning sign.
As AI advances, we must demand transparency, ethical regulations, and accountability. The future of AI must be shaped by human values—not just corporate profits.
Conclusion: Why Understanding AI Matters More Than Ever
So, after everything we’ve covered—why does AI matter so much? Why should you care?
The answer is simple: AI is reshaping the world, whether you’re ready for it or not.
- It’s changing how we work, how we communicate, and how we think about intelligence itself.
- It’s a powerful tool, but like any tool, it depends on how we use it.
- AI is not some distant, futuristic technology—it’s happening right now, in real-time.
And that’s why understanding AI is no longer optional—it’s essential.
If you:
✔️ Work in any industry—AI will impact your job.
✔️ Use the internet—AI is shaping what you see and read.
✔️ Care about ethics and privacy—AI’s decisions will affect your life.
The bottom line? The future of AI isn’t just about machines—it’s about us. It’s about how we choose to develop, regulate, and integrate AI into our society.
So the real question isn’t:
❌ “Will AI take over the world?”
The real question is:
✅ “How can we make AI work for everyone?”
And that, my friend, is why understanding AI matters more than ever.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can a beginner start learning AI?
Alright, so you want to start learning AI but have no idea where to begin? Don’t worry—you’re not alone! AI can seem overwhelming at first, but if you take it step by step, it’s totally doable, even without a tech background.
Here’s a simple roadmap to get you started:
- Understand the Basics First
- AI is just a way of making machines think like humans. Start by reading introductory books, blogs, and watching YouTube videos.
- Great beginner-friendly resources:
- “Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans” by Melanie Mitchell
- Coursera’s AI for Everyone by Andrew Ng (seriously, this is GOLD for beginners).
- Learn About AI’s Core Technologies
- AI isn’t one thing—it’s a mix of different technologies: Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Computer Vision.
- Focus on one area that excites you!
- Experiment with AI Tools
- You don’t need to be a programmer to play with AI.
- Try ChatGPT, DALL·E, RunwayML, or Google’s Teachable Machine to see AI in action.
- Take a Beginner-Friendly AI Course
- Platforms like Coursera, Udacity, and Kaggle offer free beginner courses.
- Harvard’s CS50 AI is an amazing free course if you want to dive deeper.
Personal tip? Don’t stress about understanding everything at once—just start! AI is a journey, and even experts are constantly learning. 🚀
2. What are the basics of AI?
Think of AI as a digital brain that can learn, reason, and make decisions (but in a very structured way).
At its core, AI has four main pillars:
- Machine Learning (ML): AI’s ability to learn from data and improve over time (like how Netflix learns what shows you like).
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI’s ability to understand and generate human language (like ChatGPT).
- Computer Vision: AI’s ability to see and interpret images and videos (like facial recognition).
- Robotics & Automation: AI’s ability to physically interact with the world (like self-driving cars or robotic arms in factories).
The cool part? AI isn’t magic—it’s just data and math working together in smart ways.
3. Can I self-teach myself AI?
Absolutely! AI is one of those fields where self-learning is totally possible—in fact, many AI experts are self-taught.
But here’s the deal:
- You need a structured learning path. AI is a vast field, and it’s easy to get lost.
- You need to practice. The best way to learn AI isn’t just by reading—it’s by doing.
Some practical steps to self-teach AI:
✔️ Start with AI for Everyone by Andrew Ng (free on Coursera).
✔️ Play around with AI tools like ChatGPT, TensorFlow, or Google Colab.
✔️ Join AI communities on Reddit, Kaggle, and GitHub to learn from others.
AI is like learning a new language—the more you practice, the more fluent you become.
4. Can I learn AI without coding?
Yes, you definitely can! While coding helps, there are many no-code AI tools that let you build AI models without writing a single line of code.
Some powerful no-code AI platforms:
- Teachable Machine (by Google) – Train an AI model just by uploading images!
- RunwayML – Create AI-generated videos and animations.
- Bubble.io & Lobe.ai – Build AI-powered apps without programming.
However, if you eventually want to go deeper, learning basic coding (especially Python) will give you a lot more flexibility. But for beginners, no-code AI is a great entry point!
5. Is AI a mind or a machine?
AI is just a machine—but an incredibly advanced one.
It can mimic human intelligence, but it doesn’t have emotions, self-awareness, or consciousness (at least, not yet).
Think of AI like a really smart calculator:
- It processes information, learns from data, and makes decisions.
- But it doesn’t have thoughts, feelings, or true understanding like humans do.
Some researchers argue that in the future, AI might develop some form of consciousness—but for now, it’s still just an advanced pattern-recognition machine.
6. What are the 4 elements of AI?
AI has four core elements that make it work:
- Data – AI learns from huge amounts of information (like how ChatGPT learned from billions of words).
- Algorithms – AI follows a set of rules and patterns to make decisions.
- Computing Power – AI needs powerful processors to crunch numbers and process data.
- Human Input – AI is created, trained, and fine-tuned by humans to ensure it works properly.
Without these four things, AI wouldn’t exist!
7. What are the 4 types of AI?
AI is divided into four types based on how advanced it is:
- Reactive AI – Can only respond to situations (like chess-playing AI that just follows rules).
- Limited Memory AI – Can learn from past experiences (like self-driving cars that learn from traffic patterns).
- Theory of Mind AI – Can understand emotions and human behavior (still under development).
- Self-Aware AI – AI that has consciousness (this doesn’t exist yet, but it’s a major debate in AI research!).
Right now, we mostly have Reactive AI and Limited Memory AI—but the future could bring more advanced AI models!
8. What are the 4 domains of AI?
AI is used in four major domains:
- Perception – AI that processes visuals and sounds (e.g., facial recognition, speech recognition).
- Reasoning – AI that makes decisions (e.g., fraud detection, financial forecasting).
- Learning – AI that improves over time (e.g., recommendation systems like Netflix).
- Interaction – AI that interacts with humans (e.g., ChatGPT, Siri, Alexa).
These domains shape how AI impacts everything from business to entertainment to healthcare.
9. What are the 4 knowledge representations in AI?
AI stores and processes knowledge in four main ways:
- Logical Representation – Uses rules and logic to make decisions (like a chess AI).
- Semantic Representation – Understands meaning and relationships (like Google search).
- Procedural Representation – Uses step-by-step instructions (like robot automation).
- Network Representation – Uses interconnected data structures (like neural networks in deep learning).
Each type helps AI understand and process information in different ways!