What is Artificial Intelligence? A Deep Dive into AI Definition

Table of Contents
If you’ve ever asked Siri for directions, scrolled endlessly on TikTok, or watched a perfectly curated Netflix recommendation, you’ve already encountered AI—without even realizing it. But what exactly is AI? That’s where the AI definition becomes crucial.
We hear the term “Artificial Intelligence” everywhere—from sci-fi movies where robots take over the world to business meetings where executives talk about “leveraging AI for growth.” It’s a buzzword, sure, but it’s also a groundbreaking technology that’s reshaping our lives in ways we never imagined.
Let’s be honest: AI can feel like a mystery. Some people picture super-intelligent robots taking over human jobs, while others imagine AI as a helpful assistant making life easier. The reality? AI is both exciting and complex, revolutionary yet misunderstood.
Introduction: Breaking Down the AI Definition
At its core, AI (Artificial Intelligence) refers to machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as problem-solving, learning, decision-making, and even creativity. It’s not just about automation—it’s about intelligence that evolves over time.
And here’s the kicker—AI isn’t a futuristic fantasy; it’s already here, working behind the scenes in nearly every industry. From finance and healthcare to entertainment and education, AI is everywhere.
Knowing the AI definition isn’t just about understanding a fancy term—it’s about staying informed, adapting to change, and making smarter decisions. After all, AI is already making life-changing impacts, from diagnosing cancer earlier to predicting stock market trends.
🚀 What This Article Will Cover
To truly grasp the power of AI, we’ll explore:
✔️ How AI evolved from a sci-fi dream to a real-world technology.
✔️ The different types of AI and what they mean for the future.
✔️ The ethical dilemmas and challenges AI presents.
✔️ Where AI is headed next—and what that means for humanity.
1. Understanding Artificial Intelligence: A Simple Definition

Alright, let’s get straight to it—what exactly is AI? If you ask ten different experts, you might get ten slightly different answers. But at its core, AI (Artificial Intelligence) refers to machines designed to mimic human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Imagine you’re using Google Maps to navigate a new city. It predicts the fastest route based on real-time traffic data, suggests alternative paths, and even warns you about accidents ahead. That’s AI at work—analyzing massive amounts of information to make smart decisions, just like a human would (but much faster).
But AI isn’t just about mimicking intelligence; it’s about improving and evolving over time. The more data it processes, the better it gets. Take Netflix’s recommendation engine—it learns from what you watch, how long you watch, when you pause, and even what genres you skip. Over time, it gets frighteningly good at predicting what you’ll love next. That’s AI refining itself based on experience—just like how we learn from past mistakes.
Breaking Down AI: The Three Key Components
To really understand AI definition, let’s break it down into three essential components:
- Data Processing – AI thrives on data. The more data it has, the better it performs. Every AI system needs large datasets to learn patterns.
- Algorithms & Models – AI uses advanced mathematical models to recognize patterns and make predictions. Think of this as the brain of AI.
- Automation & Adaptability – AI doesn’t just follow pre-set instructions; it learns and adapts over time. This is where AI truly becomes intelligent.
How AI Differs from Traditional Programming
A standard computer program operates in a rule-based manner: If X happens, do Y. But AI isn’t just about following rules—it’s about learning from data to generate new insights.
For example, in fraud detection, traditional software might flag transactions over $10,000 as suspicious. AI, however, analyzes past fraud patterns, learns from them, and detects anomalies beyond just high amounts—maybe it notices irregular transaction times, locations, or spending behaviors that a rule-based system would miss.
A real-world stat: AI-powered fraud detection has helped reduce credit card fraud by 30% in major financial institutions (Source: J.P. Morgan, 2023).
The AI Spectrum: Simple to Complex
AI exists on a spectrum—on one end, we have basic automation like spam filters in emails. On the other, we have AI capable of writing human-like essays .
And while AI has come a long way, we’re still far from machines that can fully replicate human thought processes. But even in its current state, AI is revolutionizing industries, and that’s why understanding AI definition is more critical than ever.
2. The Evolution of AI: From Concept to Reality
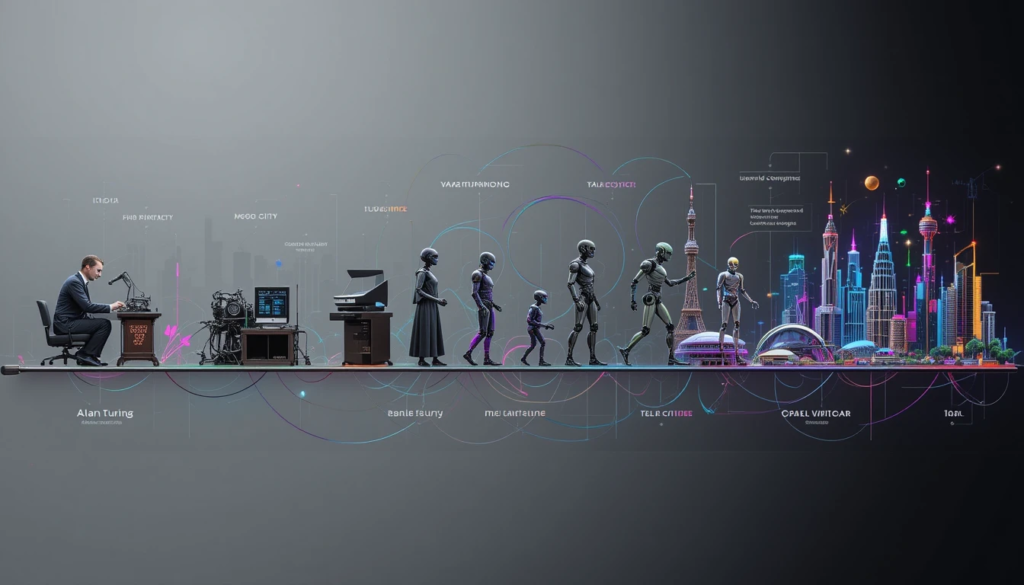
To understand where AI is today, we have to look at where it came from. AI isn’t a new concept—it’s been around for decades, even centuries if you consider early thought experiments. But the road to AI has been anything but smooth. It has seen breakthroughs, setbacks, and even periods of stagnation.
2.1 Early Theories and Philosophical Beginnings
Believe it or not, AI’s origins date back to ancient civilizations. The idea of creating artificial beings with intelligence is seen in Greek mythology (Talos, the bronze automaton), medieval robotic inventions, and even early philosophical discussions.
Fast forward to the 20th century, and thinkers like Alan Turing posed the question: “Can machines think?” His Turing Test (1950) became the foundation of modern AI—if a machine’s responses were indistinguishable from a human’s, it could be considered intelligent.
2.2 The Birth of Modern AI: 1950s–1980s
The first true AI research emerged in the 1950s, with pioneers like John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Herbert Simon. They were optimistic, predicting that AI could achieve human-level intelligence within decades.
- The Dartmouth Conference (1956) marked AI’s official birth.
- Early AI programs could solve algebra problems and play chess (IBM’s Deep Blue eventually beat world champion Garry Kasparov in 1997).
However, AI soon hit roadblocks—computers weren’t powerful enough, and data was scarce. By the 1970s, AI funding dried up, leading to the first AI winter (a period of low interest and investment in AI).
2.3 The Rise, Fall, and Resurgence of AI (1990s–Present)
AI research made a comeback in the 1990s and 2000s with machine learning and deep learning. The explosion of Big Data in the 2010s further accelerated AI’s capabilities.
Some pivotal AI moments:
- 2011 – IBM Watson defeated human champions on Jeopardy!
- 2016 – AlphaGo defeated a world champion in Go, a game once thought too complex for AI.
- 2023 – AI-powered language models like ChatGPT reached mainstream adoption, with over 180 million users in a year.
A fascinating stat: AI has increased business productivity by 40% in leading tech firms (McKinsey, 2023).
AI isn’t just evolving—it’s reshaping industries at an unprecedented pace.
3. Types of AI: From Simple Automation to Superintelligence
AI isn’t a one-size-fits-all technology. It exists in different forms, ranging from basic task automation to theoretical superintelligence that could surpass human capabilities.
3.1 Narrow AI (Weak AI): The AI We Use Today
Narrow AI refers to AI systems designed for specific tasks—and it’s everywhere.
Examples:
- Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant – Voice assistants that answer questions, set reminders, and play music.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants – AI that helps customers with common questions.
- Fraud Detection in Banking – AI models that scan millions of transactions for suspicious activity.
Narrow AI is powerful, but it has no consciousness or self-awareness—it only does what it’s trained to do.
Stat: 77% of companies are using or exploring Narrow AI solutions (Gartner, 2023).
3.2 General AI (Strong AI): The Future Goal
General AI (AGI) would have human-like intelligence, meaning it could learn, reason, and adapt across any domain—just like we do.
We’re not there yet, but researchers are working on it. If achieved, AGI could:
- Write novels as well as a human author.
- Solve complex scientific problems.
- Understand and express emotions.
But AGI raises serious ethical concerns—who controls it? How do we prevent misuse?
Experts predict AGI could emerge by 2050, but there’s no consensus.
3.3 Superintelligent AI: Science Fiction or Future Reality?
Superintelligence refers to AI far superior to human intelligence in every aspect. Think The Matrix or Skynet (Terminator)—except, hopefully, without the world domination part.
While this concept is still theoretical, AI thinkers like Nick Bostrom and Elon Musk warn that we should be cautious.
4. How AI Works: Breaking Down the Core Technologies
If AI feels like magic, that’s because we rarely see what’s happening under the hood. But AI is not magic—it’s math, data, and a lot of computing power. Let’s break it down.
4.1 Machine Learning & Deep Learning: The Brains of AI

At the heart of modern AI is machine learning (ML), which enables computers to learn patterns from data without explicit programming. Traditional software follows strict rules (if X happens, do Y). But ML models evolve based on experience—just like a human learning a new skill.
How It Works:
- Training Data – The AI model is fed huge datasets (e.g., millions of medical images to detect cancer).
- Pattern Recognition – The AI identifies common features in the data.
- Prediction & Improvement – The model makes predictions and adjusts based on results, improving over time.
💡 Example: Netflix’s recommendation engine processes petabytes of data daily, analyzing what you watch, how long, and when you pause—to fine-tune your recommendations.
Now, let’s take it up a notch—Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of ML that mimics the human brain using neural networks. Instead of learning simple patterns, DL models can analyze unstructured data like images, speech, and text.
🚀 Breakthrough Moment: In 2016, Google’s DeepMind AlphaGo defeated the world champion in Go, a game with more possibilities than atoms in the universe. That was a wake-up call—AI wasn’t just about automation; it was about true intelligence.
4.2 Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI That Understands Us
Ever wondered how Siri, Google Assistant, or ChatGPT understand and respond like humans? That’s Natural Language Processing (NLP) in action.
NLP enables AI to:
- Translate languages (Google Translate)
- Chat with users (ChatGPT, customer service bots)
- Summarize and analyze text (AI-driven journalism, legal document scanning)
💡 Stat: NLP-powered AI is expected to automate 80% of business communications by 2027 (Gartner, 2023).
But NLP is far from perfect. AI can still misunderstand context, sarcasm, or cultural nuances—like when Facebook’s AI accidentally translated “good morning” to “attack them”, causing a user’s arrest in 2017.
4.3 Computer Vision & Robotics: AI That Sees and Acts
Computer vision enables AI to interpret and analyze visual information, just like the human eye. It’s behind:
- Facial recognition (used in iPhones, airports, and security systems)
- Autonomous vehicles (Tesla, Waymo)
- Medical imaging (AI detects cancer in X-rays with 94% accuracy)
When combined with robotics, AI doesn’t just “see”—it acts. From warehouse automation (Amazon’s robots) to robotic surgery (Da Vinci Surgical System), AI-driven robots are already outperforming humans in precision-based tasks.
🚀 Mind-Blowing Fact: AI-powered robotics will cut manufacturing costs by 20-40% in the next decade (McKinsey, 2023).
4.4 The Power of Big Data & Cloud Computing
AI thrives on big data—massive amounts of information that no human could ever process alone. But where is all this data stored? That’s where cloud computing comes in.
💡 Stat: 90% of the world’s data has been created in the last two years, and AI is the key to making sense of it (Forbes, 2023).
Companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon host AI models in the cloud, allowing businesses to use AI without needing their own supercomputers.
🚀 The Takeaway: AI is not just about software—it’s about data, computing power, and algorithms working together to create intelligence that grows over time.
5. The Impact of AI: How It’s Changing the World

AI is no longer just an innovation—it’s a disruption. Whether it’s improving industries or raising ethical concerns, AI is reshaping the world in ways we never imagined.
5.1 AI in Everyday Life: From Assistants to Algorithms
Without realizing it, we interact with AI dozens of times a day:
- Voice Assistants – Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant
- Streaming Services – Netflix, Spotify, YouTube recommendations
- E-Commerce – Amazon’s AI-driven product suggestions
- Social Media – TikTok’s AI, which predicts exactly what will keep you scrolling
💡 Crazy Stat: TikTok’s AI is so powerful that users spend 52 minutes per day on average, and 90% of them keep coming back (Statista, 2023).
5.2 AI in Healthcare: Saving Lives with Data
In medicine, AI is making faster and more accurate diagnoses than human doctors. For example, AI-powered tools detect breast cancer 30% more accurately than traditional methods.
🚀 Game-Changer: AI-driven drug discovery helped develop COVID-19 vaccines in record time—what used to take years was accelerated to months.
5.3 AI in Business & Finance: The Automation Revolution
AI is automating repetitive tasks, cutting costs, and increasing efficiency. In finance, AI algorithms:
- Predict stock market trends better than human analysts
- Detect fraud in transactions, preventing billions in losses
- Power AI-driven customer service, reducing human support costs by 30%
💡 Stat: AI automation is expected to eliminate 85 million jobs but create 97 million new roles by 2025 (World Economic Forum).
5.4 Ethical Concerns: The Dark Side of AI
AI is powerful, but it’s not perfect. Major concerns include:
- Bias & Discrimination – AI can reinforce racial, gender, and economic biases.
- Privacy Issues – Facial recognition and data tracking raise surveillance concerns.
- Job Displacement – As AI automates jobs, many workers will need to reskill.
🚀 Example: A 2023 study found that AI-powered hiring tools discriminated against women and minorities because they were trained on biased historical data.
6. The Future of AI: What’s Next?
AI is moving fast—so where do we go from here?
6.1 Explainable AI: Making AI Less of a Black Box
Today’s AI works, but we often don’t know why it makes certain decisions. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to make AI more transparent.
💡 Key Trend: Governments are pushing for AI regulations to ensure fairness and accountability.
6.2 AI and Human Collaboration: The Rise of Augmented Intelligence
Instead of replacing humans, AI is evolving into a tool that enhances human abilities. Imagine AI-assisted doctors, lawyers, and teachers—AI will empower professionals rather than replace them.
🚀 Prediction: By 2030, AI-augmented workforces will be the norm, blending human creativity with AI’s computational power.
6.3 The AGI Debate: Will AI Ever Think Like Us?
General AI (AGI) is the holy grail—an AI that can reason, plan, and make decisions like a human. But when will it happen?
💡 Elon Musk Prediction: AGI could emerge by 2029, while others believe it’s 50+ years away.
The real question is: Can we control AGI once it exists? If AI surpasses human intelligence, who makes the rules?
Conclusion: AI Definition – A Revolution, Not Just a Concept
We started with a simple question: What is AI? Now, after peeling back the layers, it’s clear that AI isn’t just a tool—it’s a revolution.
From voice assistants predicting what you need before you ask, to AI-powered doctors diagnosing diseases with pinpoint accuracy, AI has already woven itself into the fabric of our lives. And it’s just getting started.
When we talk about AI definition, we’re not just defining a technology—we’re defining the future of humanity. AI has the power to:
- Enhance creativity (AI-generated art and music)
- Increase efficiency (automating repetitive tasks in industries)
- Save lives (AI in healthcare detecting diseases faster)
- Revolutionize learning (personalized AI tutors for students)
But it also raises big questions:
- Will AI replace human jobs or create new ones?
- How do we ensure AI remains ethical and unbiased?
- At what point does AI become too powerful?
Let’s be real—AI isn’t all sunshine and rainbows. While it offers incredible opportunities, it also presents significant risks. Job displacement, privacy concerns, and AI-generated misinformation are all issues we must address.
So, what’s the next chapter in AI’s story? Here are some bold predictions:
🚀 By 2030, AI will be deeply integrated into everyday life, from personalized AI assistants to AI-driven mental health therapy.
🚀 Self-driving cars will reduce traffic accidents by over 90%, potentially saving millions of lives.
🚀 AI will play a massive role in climate change solutions, optimizing energy use and reducing waste.
But perhaps the biggest question is: Will AI ever achieve human-level intelligence (AGI)—or even surpass it?
Some experts say we’re decades away from AGI. Others believe we’ll see it within our lifetime. Whatever happens, one thing is certain: AI is not slowing down.
The AI definition goes beyond machines and algorithms—it’s about how we, as humans, shape this technology. AI has the potential to amplify human intelligence, accelerate progress, and solve global challenges—but only if we use it responsibly.
So, what do you think? Is AI a force for good, a potential danger, or something in between? The future isn’t set in stone—it’s up to us to decide how AI will shape our world.
FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About AI Definition
AI is a fascinating yet complex topic, and naturally, many questions arise when discussing its definition, capabilities, and future. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most frequently asked questions about AI definition and what it means for the world.
1. What is the simplest AI definition?
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, refers to machines or software that can think, learn, and make decisions similarly to humans. Instead of following strict, pre-programmed rules, AI uses data, patterns, and algorithms to solve problems, recognize speech, and even understand language.
2. How does AI work?
AI works by processing huge amounts of data and identifying patterns using advanced algorithms. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Collecting Data – AI gathers and analyzes information.
- Training Models – AI “learns” from data to improve its predictions.
- Making Decisions – AI uses logic, probabilities, or deep learning to make smart choices.
- Improving Over Time – AI refines itself by continuously learning from new data.
A great example is Netflix’s AI, which learns your preferences and recommends shows based on what you’ve watched before.
3. What are the main types of AI?
AI is generally classified into three types:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI) – Specialized in one task (e.g., Siri, ChatGPT, self-driving cars).
- General AI (AGI) – AI with human-like reasoning (still theoretical).
- Superintelligent AI – AI that surpasses human intelligence (a future possibility).
Right now, we only have Narrow AI—but researchers are working towards General AI.
4. How is AI different from automation?
AI is not the same as basic automation.
- Automation follows fixed instructions (e.g., a robot in a factory assembling cars).
- AI learns and adapts (e.g., Tesla’s self-driving AI learning from real-world driving data).
The key difference? AI gets smarter over time, while automation stays the same.
5. Can AI think like a human?
Not yet. Current AI can process information faster than humans, but it lacks true understanding, emotions, and self-awareness. It follows logic but doesn’t have real creativity or consciousness.
However, researchers are working on Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), which could think and reason like a human.
6. Where do we use AI in everyday life?
AI is already everywhere, even if you don’t notice it. Some everyday examples include:
✅ Google Search & Voice Assistants (Siri, Alexa)
✅ Netflix & Spotify recommendations
✅ AI chatbots in customer service
✅ Facial recognition on smartphones
✅ Self-driving cars
✅ Fraud detection in banking
It’s no longer the future—AI is part of our daily lives right now.
7. Will AI take over human jobs?
AI will replace some jobs, but it will also create new ones. Experts predict that AI could eliminate 85 million jobs by 2025—but it will also create 97 million new jobs (World Economic Forum).
Jobs involving creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making will remain in demand. Instead of replacing all workers, AI is more likely to enhance human capabilities.
8. Can AI be dangerous?
AI is not inherently dangerous, but it does have risks, such as:
- Bias & Discrimination – AI can reflect human biases if trained on biased data.
- Job Losses – AI automation may disrupt industries.
- Misinformation – AI-generated content can be used for deepfakes.
- Lack of Control – Superintelligent AI could surpass human oversight.
That’s why AI ethics and regulations are crucial to ensure responsible AI development.
9. What is the future of AI?
The future of AI includes:
🚀 Smarter AI Assistants – AI that understands human emotions.
🚀 Self-Driving Cars – AI reducing traffic accidents.
🚀 AI in Healthcare – Diagnosing diseases faster than doctors.
🚀 AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) – AI that can think like a human (still a long way off).
By 2030, AI will be a fundamental part of industries, making human-AI collaboration the norm.
10. How can I learn more about AI?
If you want to dive deeper into AI, here are some great ways to get started:
📚 Books – Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans (Melanie Mitchell)
🎓 Online Courses – Coursera, Udacity, and edX offer free AI courses.
📢 Tech Blogs & News – Keep up with AI advancements on blogs like OpenAIJournal (your AI news community 😉).